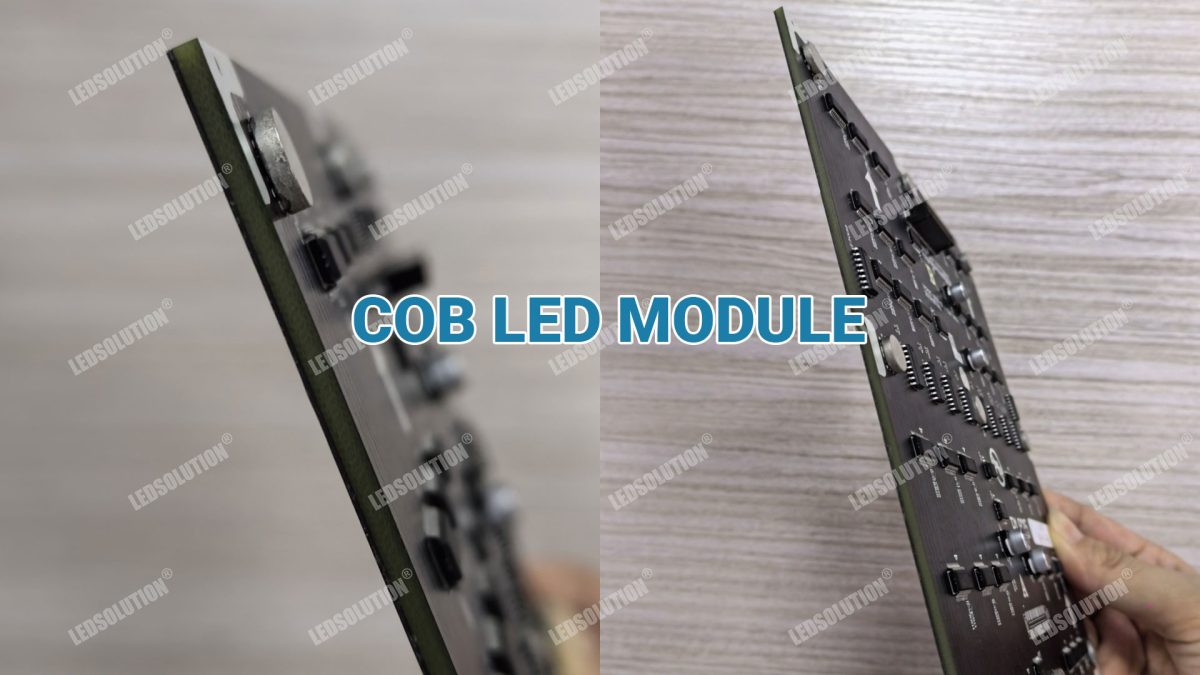
As LED technology evolves, new encapsulation methods like COB (Chip-On-Board) and GOB (Glue-On-Board) have emerged, each with its unique advantages and applications. Deciding which is better depends on your specific requirements. Below, we explore the key differences, advantages, and disadvantages of both technologies.
What is COB (Chip-On-Board)?
COB technology involves mounting LED chips directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB) and then covering them with an epoxy layer for protection. This approach eliminates the need for individual packaging of each LED, making the design compact and efficient.

Advantages of COB–>>
- High Durability: COB is extremely robust, providing resistance against impact, moisture, and dust.
- Enhanced Heat Dissipation: The direct mounting on the PCB ensures better thermal management, improving the lifespan of the LEDs.
- Better Visual Quality: COB technology reduces the gaps between LEDs, resulting in seamless displays with higher uniformity.
- Slim Design: The compact nature of COB modules allows for thinner, more lightweight LED panels.
- Improved Viewing Angle: Offers wide viewing angles with minimal color distortion.
- Repair Complexity: Damaged LED chips can be challenging to repair, often requiring the replacement of the entire module.
- Cost: The manufacturing process is more complex, leading to higher production costs.
- Brightness Limitations: Compared to other technologies, COB displays may not achieve the highest brightness levels.
<<–Disadvantages of COB
What is COB (Chip-On-Board)?
GOB technology involves applying a transparent glue layer over traditional SMD (Surface-Mounted Device) LEDs. This layer protects the LEDs from physical damage and environmental factors while maintaining their visibility.

- Strong Protection: GOB provides excellent resistance to dust, water, and physical impact, making it ideal for rugged environments.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to COB, GOB is less expensive to produce, as it utilizes traditional SMD technology with added protection.
- High Brightness: GOB displays maintain the brightness levels typical of SMD-based LEDs.
- Easy Maintenance: The underlying SMD technology allows for easier repair and replacement of damaged components.
<<–Advantages of GOB
Disadvantages of GOB–>>
- Heat Dissipation Issues: The glue layer can hinder heat dissipation, potentially reducing the lifespan of LEDs if not managed properly.
- Yellowing Over Time: The glue layer may degrade and yellow with prolonged exposure to UV light, affecting display clarity.
- Uneven Surface: Achieving a perfectly smooth surface is challenging, which can impact the aesthetic quality of the display.
COB vs. GOB: A Feature Comparison
|
Feature |
COB |
GOB |
|
Durability |
Highly durable |
Durable but prone to glue aging |
|
Heat Dissipation |
Excellent |
Moderate |
|
Brightness |
Moderate |
High |
|
Visual Quality |
Seamless and uniform |
Dependent on glue application |
|
Maintenance |
Complex (entire module repair) |
Easier (individual chip repair) |
|
Cost |
Higher production cost |
Lower production cost |
|
Weight |
Lightweight |
Slightly heavier due to glue |
COB vs. GOB: A Feature Comparison
Choose COB If:
- You need a highly durable display for harsh environments.
- Seamless visual quality and uniformity are top priorities.
- Weight and space-saving design are critical.
Choose GOB If:
- Budget constraints are a concern.
- You require high brightness and easier maintenance.
- The display will be exposed to potential physical damage but not prolonged UV exposure.
Conclusion
Both COB and GOB technologies have their strengths, and the choice depends on your application. COB offers superior durability, heat dissipation, and seamless design but at a higher cost. On the other hand, GOB balances cost-effectiveness with protection and is ideal for general-purpose use where brightness and repairability are essential.
Would you like additional details on either technology or examples of their applications? Contact the LEDSOLUTION team today to find the perfect solution for your needs!